Terraforming 101
Submitted by Charles Frost on Mon, 11/12/2007 - 21:58.
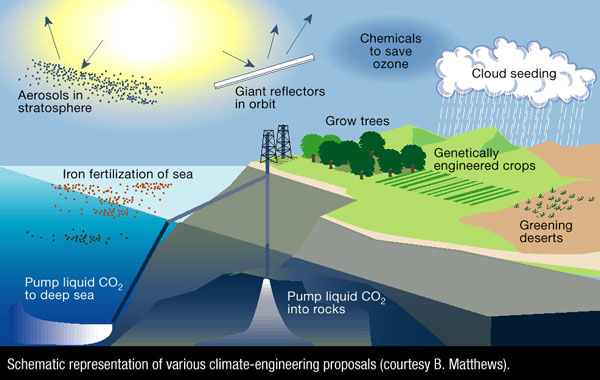
Giving Climate Change a KickBy Eli Kintisch
ScienceNOW Daily News
9 November 2007CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS--Top climate scientists have cautiously endorsed the need to study schemes to reverse global warming that involve directly tinkering with Earth's climate. <--!break--> Their position on geoengineering, which will likely be controversial, was staked out at an invitation-only meeting that ended here today. It's based on a growing concern about the rapid pace of global change and continued anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases. "In this room, we've reached a remarkable consensus that there should be research on this," said climate modeler Chris Bretherton of the University of Washington, Seattle, during a morning session today. Phil Rasch, a modeler with the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colorado, underscored the point. "We're not saying that there should be geoengineering, we're saying there should be research regarding geoengineering." No formal statement was released at the meeting, which was organized by Harvard University and the University of Calgary, but few of the 50 scientists objected to the idea. The field of geoengineering has long been big on ideas but short on respect. Some of the approaches that researchers have dreamed up include launching fleets of space-based shades to dim the sunlight hitting Earth or altering the albedo of the ocean with light-colored reflectors. Perhaps the best-known idea is to pump aerosols into the stratosphere to mimic the cooling effect of volcanoes. But there's been scant support from mainstream scientists, many of whom fear that even mentioning the g-word could derail discussion of carbon-emissions cuts. Others worry that technological tinkering might backfire. "I just accepted on faith as an environmental scientist that this had to be a bad idea," said Harvard's Scot Martin, who said he was reluctantly coming around. Harvard geochemist Daniel Schrag and physicist David Keith of the University of Calgary thought that geoengineering deserved a closer look (Science, 26 October, p. 551). In an opening presentation yesterday, Schrag explained that extensive, rapid melting of arctic sea ice (ScienceNOW, 2 May) and the fact that the world's 2005 and 2006 carbon emissions from fossil fuels were higher than predictions by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change are forcing the hands of climate scientists. Schrag also fears that when countries are faced with the prospect of even more drastic environmental change, they will turn to geoengineering regardless of whether the consequences are known. "We're going to be doing this if we're afraid of something really bad happening, like the Greenland ice sheet collapsing," he said. The degree of scientific uncertainty was clear throughout the 2-day meeting. In a discussion of existing models, climate modeler Ken Caldeira of the Carnegie Institution of Washington in Stanford, California, concluded that reducing the intensity of sunlight hitting Earth by about 2% could "markedly diminish" the massive warming effects of an atmosphere with a carbon dioxide content of 560 parts per million (ppm). (The current level is about 385 ppm.) But over lunch, researchers debated the analysis. "You know you can get some sea ice back," Caldeira said to David Battisti of the University of Washington, Seattle. "I don't know that," Battisti retorted, explaining that Caldeira's model assumed a so-called slab ocean, which does not include the heat circulation patterns that help determine the fate of polar ice. And then there are the risks. Harvard paleoclimate scientist Peter Huybers told his colleagues during one session that understanding of the world's climate may not be sufficient to properly wield geoengineering tools. "We should be humble about how much we know about the climate system," Huybers said. Most of the discussion focused on whether to jump-start what has been an anemic research agenda with no public financing. Some participants said that they were spurred into action by a paper that appeared in Climatic Change last year, in which Nobelist Paul Crutzen called for geoengineering research (Science, 20 October 2006, p. 401). Others were swayed more recently. Just 2 weeks ago, modeler Raymond Pierrehumbert of the University of Chicago in Illinois, writing on the RealClimate blog, compared discussing geoengineering to "having a shiny new toy" and told climate scientists to "get back to the serious business of trying to figure out how to economically reduce global CO2 emissions." At the meeting, however, Pierrehumbert urged scientists to study the problem as a supplement to cutting greenhouse gas emissions, although he called for a 10-year moratorium on any geoengineering. "To the extent I've changed my mind a little bit," Pierrehumbert explained to Science, the reason is the ease with which countries could embark on geoengineering. Harvard climate researcher James Anderson told the group that the arctic ice was "holding on by a thread" and that more carbon emissions could tip the balance. The delicacy of the system, he said "convinced me of the need for research into geoengineering," Anderson said. And 5 years ago? "I would have said it's a very inappropriate solution to the problem."Photo from: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v409/n6818/images/409420aa.2.jpg
|
Sounds like fun, but I'll just plan on dying
I hope we all go quickly, but I suspect it will be more like today, when worse than usual weather sinks a dozen ships, dumping 10,000s of gallons of oil into our limited waters, every day, somewhere on Earth, until its over for everyone... death by 1,000,000,000,000s of cuts over very few years. But think of all the money to be made by smart capitalists like Gore in the mean time...
Disrupt IT
Wow, What A Gloomy Outlook
Sometimes the "real world" looks bad, and it just might be as bad as it looks, but you can't give up hope.
We have seen this "world" thru some hard times.
I am sure that the "Black Death" back in the 1600's looked like the "end of the world" to many people, but they just kept on...
The folks in London just "kept on living" during "The Blitz" during the WWII. Some of us wouldn't be here had that not persisted in spite of reason.
Some people who were building bomb shelters in the 60's during the Cold War were expecting to need to use them. Fortunately they didn't.
Our children, and their children will not be giving up hope, as our forefathers didn't before us, therefore we cannot.
Another Doomy & Gloomy Thought...
NASA blasted for ignoring smaller asteroids